Part Two: Designing Products for Rotational Molding
Tolerances
Part Two: Designing Products for Rotational Molding
TolerancesTolerances
It is prudent for the designer of rotomolded parts to be fully cognisant of the known shrinkage characteristics of plastic materials, especially polyethylene. As discussed in a previous section, the shrinkage rate can be affected by a combination of different factors, so the achievement of dimensional precision is likely to be challenging. Whilst it may be possible to hold tight tolerances on a few specific part dimensions, it is usually not possible to simultaneously hold a multitude of part dimensions to tight tolerances.
Full dimensional precision in mold manufacture may be an issue, depending on the type of construction method. Whilst CNC molds can be made to very tight tolerances, cast aluminium molds will be subject to a greater dimensional variance and fabricated molds will generally have the least precision.
In general, small parts will be easier to hold to tolerance than large and thin-walled parts will be easier than thick-walled parts.
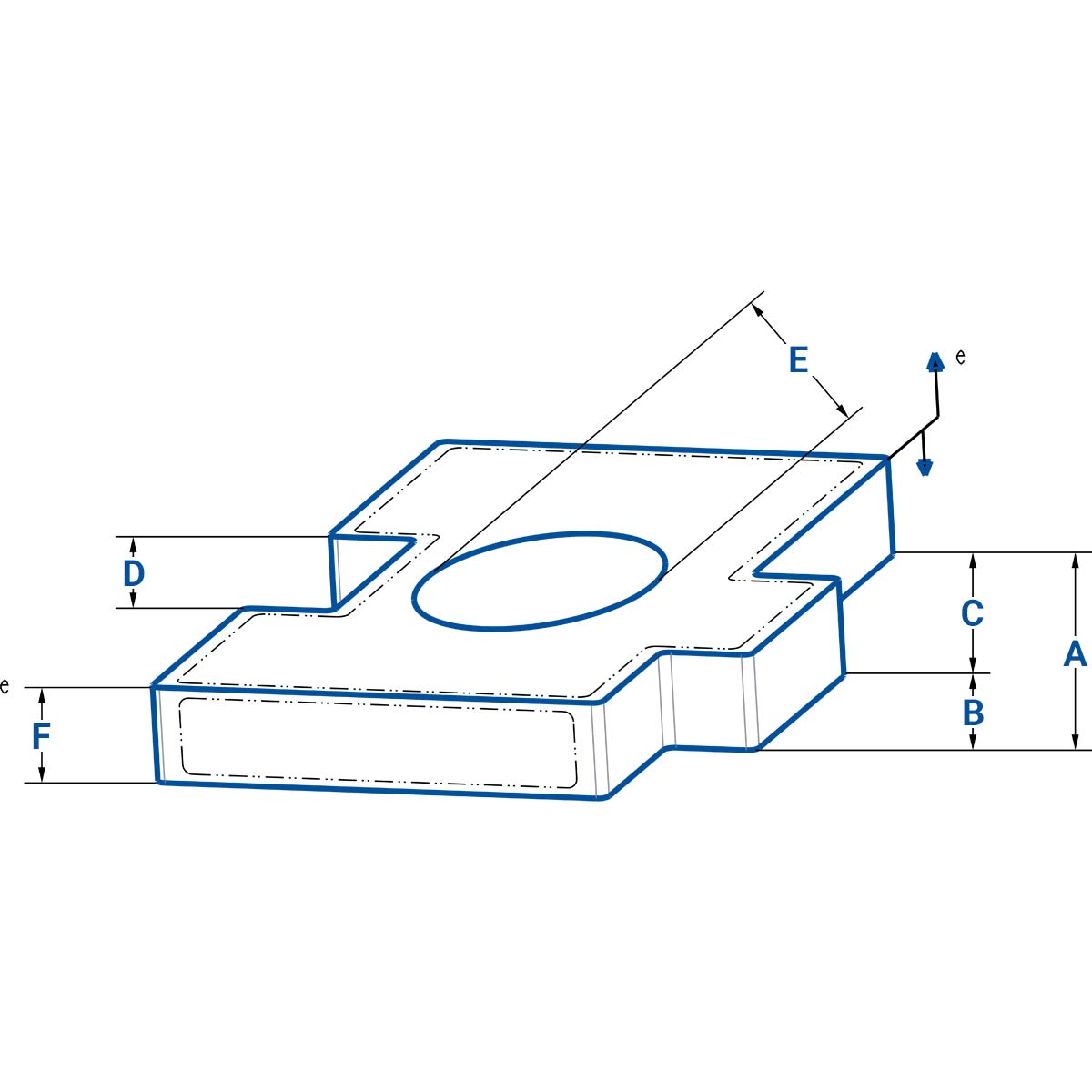
The outside dimensions of a rotomolded part (Figs 34 Items A, B, C & F) will be free to draw away from the inside surface of the mold as the plastic shrinks during cooling; they are free-formed. To this extent, their behavior may be difficult to control. The inside sections (Items D & E) will shrink down on to the cavity and will therefore be easier to control.
The shrinkage characteristics of rotomolding materials may vary from batch to batch, from base resin grade to grade and between color options. The use of reprocessed fractions, or off-grade material, will further increase the potential for variability.
In terms of part tolerances, a well-controlled and monitored molding method will help to minimize process variables. The other helpful manufacturing technique will be the use of shrinkage jigs, post-molding.
Process consistency includes regular mold maintenance, to ensure that the behavior of parting lines is not affected by material build-up or general wear-and-tear.
Shrinkage effects can be affected by the quality of the release surface of the mold cavity. As well as good mold maintenance, this can be affected by the mold release method utilized. A permanent coating (eg Teflon) applied to the mold should, in principle, aid consistency, provided that it is well maintained and not degraded by misuse. If semi-permanent mold release agents are used, a regular application schedule and standardized application techniques will both be helpful.
Recommended tolerances for polyethylene rotogrades are shown below (dimensions: inches / inch):
- Ideal design: ±0.010 (inside sections) ±0.020 (outside sections)
- Commercial design: ±0.008 (inside sections) ±0.010 (outside sections)
- Precision design: ±0.004 (inside sections) ±0.005 (outside sections)
